线性回归公式
线性回归公式:
$$ { \hat y=\omega_0+\omega_1x_1+...+\omega_px_p } $$
说明:
- 数学上,我们把$\omega=(\omega_1,...,\omega_p)$称为系数(coefficient),$\omega_0$称为截距(intercept)。
- 在机器学习里面,$y$是我们要预测的目标变量,$x_i$代表每个特征变量。
- $y$上面的小标记(hat)表示式子右边是对左边的最佳估计。
- 上面的式子也可以表示为向量形式:$\hat y=X\omega$。
- 这里的线性回归方程是超平面的线性回归方程。
所以线性回归的模型很简单,就是一个超平面方程,接下来需要做的就是根据已知的数据(即已知$y_i$和$x_i$)来求系数$\omega_i$和截距$\omega_0$。根据求解方式(称为目标函数或损失函数)的不同,产生了很多线性模型。
普通最小二乘法
最常见的线性模型就是普通最小二乘法(Ordinary Least Squares, OLS)模型,即最小化预测值和真实值之间的差,为了避免正负值相互抵消,使用差的平方和。也就是说OLS的目标函数如下:
$$ { \underset{{\omega}}min||X\omega-y||_2^2 } $$
对$\omega$求导并令其等于0得到:
$$ { \hat \omega=(X^TX)^{-1}X^Ty } $$
这样我们便得出了$\omega$的一种计算方法。不过从式子中可以看到需要对矩阵求逆,所以OLS只适用于矩阵存在逆矩阵的情况。也就是说OLS要求模型的各个特征之间要是相互独立的(且必须是方阵,因为只有方阵可能有逆矩阵,即样本点一定不能小于特征数),否则矩阵将会是奇异的(singular:一个$n*n$矩阵若不存在乘法逆元,则称为奇异的)。
岭回归
简单来说,岭回归(Ridge regression)就是在矩阵$X^TX$上加了一个$\alpha{I}$从而使得矩阵非奇异,进而能对$X^TX+\alpha{I}$求逆,这样就解决了OLS所存在的问题。因为引入的单位矩阵$I$对角线上面值为1,其它值为0,像一道“岭”一样,因此得名。
岭回归的目标函数为:
$$ { \underset{\omega}min(||X\omega-y||_2^2+\alpha{||\omega||_2}^2) } $$
通过引入惩罚项(penalty)来减少不重要的参数,这种技术在统计学里面称为缩减(shrinkage)。维基百科里面的描述如下:
In regression analysis, a fitted relationship appears to perform less well on a new data set than on the data set used for fitting.[1] In particular the value of the coefficient of determination 'shrinks'. This idea is complementary to overfitting and, separately, to the standard adjustment made in the coefficient of determination to compensate for the subjunctive effects of further sampling, like controlling for the potential of new explanatory terms improving the model by chance: that is, the adjustment formula itself provides "shrinkage." But the adjustment formula yields an artificial shrinkage, in contrast to the first definition.
岭回归里面就是通过引入$\alpha$(≥0)来限制所有$\omega$的和,$\alpha$值非常小时,系数与普通回归一样;$\alpha$非常大时,所有回归系数缩减为0(缩减的量达到最大),一般我们需要在中间某处找到使得预测结果最好的$\alpha$的值。代码演示如下(代码来自here):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
# X is the 10x10 Hilbert matrix
X = 1. / (np.arange(1, 11) + np.arange(0, 10)[:, np.newaxis])
y = np.ones(10)
# #############################################################################
# Compute paths
n_alphas = 200
alphas = np.logspace(-10, -2, n_alphas)
coefs = []
for a in alphas:
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=a, fit_intercept=False)
ridge.fit(X, y)
coefs.append(ridge.coef_)
# #############################################################################
# Display results
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(alphas, coefs)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim()[::-1]) # reverse axis
plt.xlabel('alpha')
plt.ylabel('weights')
plt.title('Ridge coefficients as a function of the regularization')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()运行结果:
Lasso回归
Lasso全称为The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator。其原理和岭回归类似,不过其惩罚项采用L1范数(L1-norm):
$$ { \underset{{\omega}}min(\frac{1}{2n_{sample}}||X\omega-y||_2^2+\alpha{||\omega||_1}) } $$
和岭回归相比,Lasso虽然只是将L2范数换为了L1范数,但其产生的影响正好相反,我们将岭回归中的代码简单修改如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
# X is the 10x10 Hilbert matrix
X = 1. / (np.arange(1, 11) + np.arange(0, 10)[:, np.newaxis])
y = np.ones(10)
# #############################################################################
# Compute paths
n_alphas = 200
alphas = np.logspace(-10, -2, n_alphas)
coefs = []
for a in alphas:
lasso = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=a, fit_intercept=False)
lasso.fit(X, y)
coefs.append(lasso.coef_)
# #############################################################################
# Display results
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(alphas, coefs)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim()[::-1]) # reverse axis
plt.xlabel('alpha')
plt.ylabel('weights')
plt.title('Lasso coefficients as a function of the regularization')
plt.axis('tight')
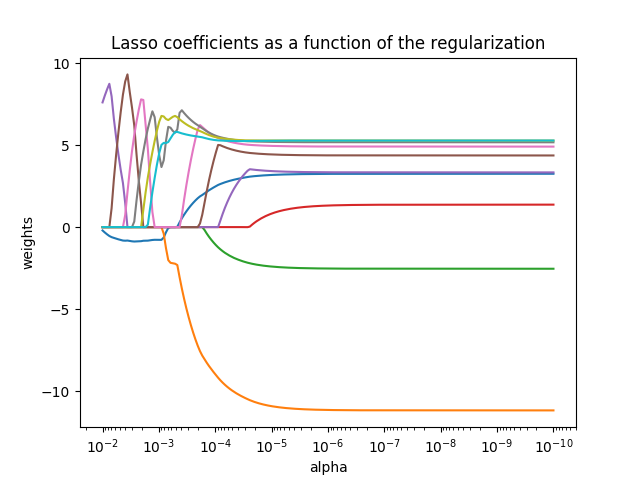
plt.show()运行结果如下:
可见与岭回归正好相反,Lasso中当$\alpha$足够小时,系数会被缩减到0.所以Lasso模型一般偏向于产生比较少的非零系数。
Elastic Net回归
Elastic Net回归可以说是Ridge和Lasso的并集,其目标函数为:
$$ { \underset{{\omega}}min(\frac{1}{2n_{sample}}||X\omega-y||_2^2+\alpha\rho{||\omega||_1}+\frac{\alpha(1-\rho)}{2}||\omega||_2^2) } $$
可见Elastic Net同时采用了L1和L2范数作为正则化,这样使得Elastic Net集成了Ridge和Lasso的功能。可以看到,当$\rho=1$的时候,Elastic Net就是Lasso。有一点不同的是,当有多个特征相关时,Lasso会从相关的特征里面随机选一个,而Elastic Net则会都选用。
References:
 NYC's Blog
NYC's Blog 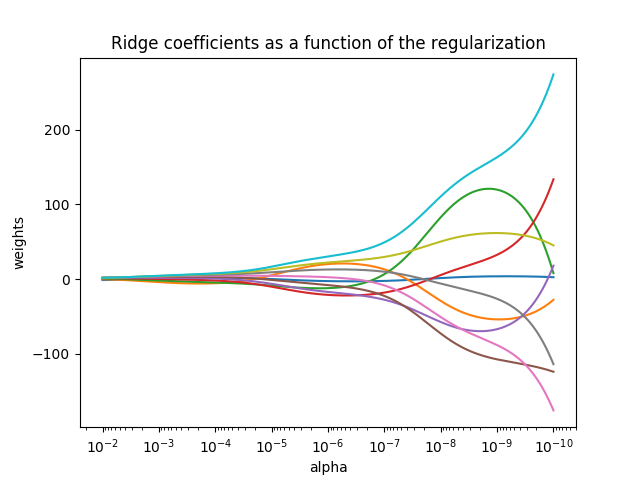
评论已关闭